Berkeley Ca Earthquakes A Comprehensive Guide
Lead: Nestled in the heart of the seismically active San Francisco Bay Area, Berkeley, California, faces a persistent and significant earthquake risk. With the infamous Hayward Fault running directly beneath the city and its proximity to the San Andreas Fault, understanding local seismic activity is not merely an academic exerciseit is an essential component of urban living and community resilience. This comprehensive guide aims to equip residents and interested parties with critical insights into Berkeley's earthquake landscape, offering a deep dive into its geological context, historical tremors, and, most importantly, actionable strategies for effective preparedness. Readers will gain a robust understanding of the risks involved and the steps necessary to safeguard themselves and their community against future seismic events.
What Is Berkeley CA Earthquakes
This guide serves as a detailed resource for anyone seeking to understand the unique seismic challenges presented by Berkeley's geographical location. It outlines the specific geological features that contribute to the city's earthquake risk, notably the Hayward Fault, which is one of the most active and urbanized faults in California. The guide synthesizes information from geological surveys, seismological research, and emergency management protocols to create a singular point of reference. Key aspects covered include:
- Geological Overview: Explanation of tectonic plate movements and the specific faults impacting Berkeley.
- Seismic History: A review of significant earthquakes that have affected the region, providing context for potential future events.
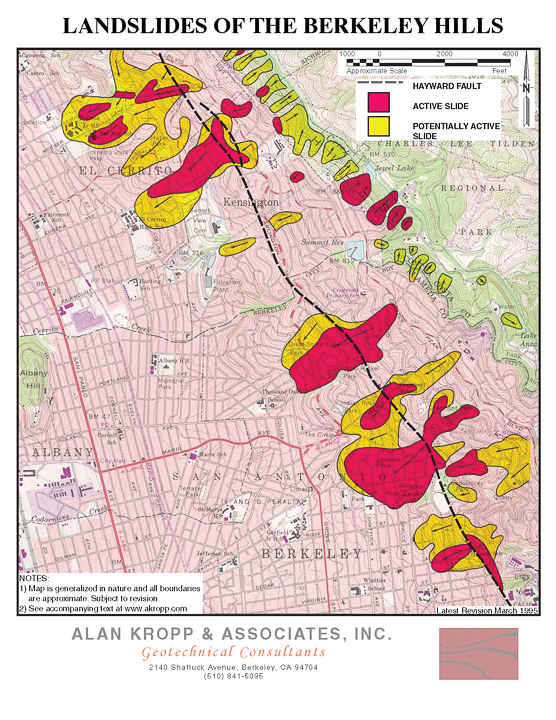
- Risk Assessment: An analysis of the types of hazards associated with earthquakes, such as ground shaking, liquefaction, and landslides.
- Preparedness Strategies: Practical, step-by-step advice for individuals, families, and businesses to mitigate risks.
- Official Resources: Pointers to government agencies and academic institutions offering further support and information.
Essentially, its a living document that empowers individuals to move beyond mere awareness to proactive readiness, fostering a culture of safety throughout the Berkeley community.
Why Berkeley CA Earthquakes
While "trending" in a traditional social media sense might not fully capture the essence, the subject of Berkeley's earthquake preparedness is perpetually relevant and critically important, ensuring it remains a constant point of interest. The continuous tectonic activity beneath the Bay Area, coupled with scientific advancements that refine seismic hazard assessments, keeps earthquake preparedness at the forefront of public consciousness. For instance, recent studies continually update probabilities of significant quakes on the Hayward Fault, reminding residents of the ever-present threat. Furthermore, increasing population density and urban development mean that more people and infrastructure are potentially exposed to seismic hazards, amplifying the need for informed action and robust preparation. Historical reminders, such as the anniversary of the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake, also serve to renew interest in safety protocols. This ongoing relevance ensures that comprehensive guides on Berkeley's earthquake risks are not just popular, but essential reading for residents and policymakers alike.
Dates, Locations, or Key Details
Berkeley's earthquake reality is defined by specific geological features and historical events. The city sits directly atop the Hayward Fault, a major right-lateral strike-slip fault that traverses a densely populated corridor of the East Bay. This fault is particularly concerning due to its "creeping" natureit moves slowly and continuously, but segments can lock up and build stress, leading to a potentially large earthquake. The most notable historical event on the Hayward Fault was the 1868 Hayward Earthquake, estimated to be magnitude 6.87.0, which caused widespread damage and was dubbed "The Great San Francisco Earthquake" prior to the more famous 1906 event. Scientists now believe there is a significant probability (often cited around 30% in the next 30 years) of a magnitude 6.7 or greater earthquake on the Hayward Fault.
Additionally, Berkeley is situated in close proximity to the larger San Andreas Fault system, which famously ruptured in 1906 (magnitude 7.9) and 1989 (Loma Prieta, magnitude 6.9). While further away, a major San Andreas event would still significantly impact Berkeley. Key organizations providing ongoing data and expertise include the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), the California Geological Survey (CGS), and the UC Berkeley Seismological Laboratory, which operates a vast network of seismic sensors across Northern California. These institutions continually monitor micro-seismicity and conduct research crucial for understanding regional seismic hazards.
How To Get Involved or Access Berkeley CA Earthquakes
Engaging with earthquake preparedness involves both accessing information and taking practical steps. Heres how residents can become more informed and prepared:
- Access Official Information: Start with the City of Berkeleys Office of Emergency Services website, which provides local-specific guidance, hazard maps, and emergency plans. The USGS and CGS websites offer broader scientific data and earthquake safety tips.
- Create an Emergency Plan: Develop a family communication plan, establish out-of-state contacts, and designate meeting points. Discuss what to do during and after a quake.
- Assemble Emergency Kits: Prepare a "Go Bag" with essentials like water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, medications, a flashlight, and a whistle. Have a larger home kit with a week's supply of resources.
- Secure Your Home: Anchor tall furniture, water heaters, and appliances. Install cabinet latches. Consider retrofitting older homes to withstand seismic forces, especially if they have unbraced cripple walls or are built on an unreinforced masonry foundation.
- Participate in Community Programs: Join local Community Emergency Response Team (CERT) training. These programs teach basic disaster response skills, allowing individuals to help their families and neighbors in an emergency.
- Stay Informed: Sign up for emergency alerts from the City of Berkeley and utilize resources like ShakeAlert, which provides early warning for incoming tremors.
What To Expect
- Clear Understanding of Risk: Gain a factual basis for the specific seismic threats Berkeley faces, moving beyond general anxiety to informed awareness.
- Actionable Preparedness Steps: Receive practical, easy-to-follow advice for securing homes, assembling emergency supplies, and creating family safety plans.
- Access to Verified Resources: Learn where to find reliable, official information from geological experts and emergency management agencies.
- Increased Sense of Safety: Feel more secure through proactive preparation, knowing specific actions can significantly mitigate risks and enhance post-quake recovery.
The Broader Impact of Berkeley CA Earthquakes
The continuous focus on Berkeley's earthquake risk significantly influences urban planning, infrastructure development, and community resilience. City planners and engineers integrate seismic considerations into every major project, from building codes to public infrastructure upgrades. Strict building codes in California, informed by seismological research, ensure that new constructions are designed to withstand significant shaking. Existing infrastructure, such as bridges, utility lines, and public buildings, undergoes periodic seismic retrofitting to enhance safety and operational continuity post-quake. This proactive approach aims to minimize economic disruption and accelerate recovery. The guide's emphasis on individual and community preparedness also fosters a stronger, more self-reliant populace, capable of responding effectively in the immediate aftermath of an event and supporting broader recovery efforts.
Living in the Bay Area means living with active geology. Understanding the specific risks posed by faults like the Hayward is not just academic; it's fundamental to community safety and resilience. Comprehensive guides like this empower residents to be part of the solution. Dr. Elena Rodriguez, Seismologist, UC Berkeley Seismological Laboratory.
Economic or Social Insights
Earthquake preparedness and the potential for a major seismic event have profound economic and social implications for Berkeley. Economically, the continuous investment in seismic retrofits for both public and private buildings represents a significant financial commitment, yet it is dwarfed by the potential cost of inaction. A major earthquake could cause billions in property damage, business interruption, and infrastructure repair, impacting local and regional economies. Insurance premiums in high-risk areas reflect this, often being a substantial cost for property owners. Socially, the constant awareness of earthquake risk shapes community life. There is a strong emphasis on community-level preparedness through programs like CERT, fostering social cohesion and volunteerism. The topic also influences migration patterns and housing decisions, though the Bay Area's economic opportunities often outweigh seismic concerns for many. Insights from regional economic studies, like those often cited by the Bay Area Council or local government reports, consistently highlight the long-term economic benefits of proactive disaster mitigation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Berkeley CA Earthquakes
- What is Berkeley CA earthquakes a comprehensive guide? This is a detailed informational resource designed to educate Berkeley residents and stakeholders about the specific seismic hazards in their area, including geological background, historical events, and practical strategies for earthquake preparedness and response.
- Why is understanding Berkeley's earthquake risk important? Berkeley is uniquely situated directly on the Hayward Fault and close to the San Andreas Fault, making it highly susceptible to significant seismic activity. A thorough understanding of these risks is crucial for personal safety, protecting property, and ensuring community resilience.
- How can residents prepare for earthquakes? Key preparedness steps include assembling emergency kits (Go Bag and home supply), securing household items, developing a family communication plan, retrofitting homes for seismic safety, and participating in local emergency training programs like CERT.
- What official resources are available? Authoritative sources include the City of Berkeleys Office of Emergency Services, the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), the California Geological Survey (CGS), and the UC Berkeley Seismological Laboratory. These organizations provide scientific data, safety guidelines, and local emergency information.
- What does a comprehensive guide offer? It provides a holistic approach to earthquake safety, covering scientific explanations of local faults, historical context of past quakes, step-by-step practical preparedness advice, and connections to official resources for ongoing support and information, all aimed at fostering a prepared and resilient community.
Conclusion
The reality of living in Berkeley, California, is inextricably linked to the dynamic geology of the region. Acknowledging and preparing for potential earthquakes is not a matter of fear, but of informed responsibility and proactive community building. This comprehensive guide underscores that while seismic events are inevitable, their impact can be significantly mitigated through education, planning, and collective action. By understanding the specific risks posed by faults like the Hayward and leveraging the wealth of available resources, residents can transform uncertainty into preparedness, safeguarding lives and livelihoods. Being informed and prepared is the most effective defense against the natural forces at play.